
Looking for a new role can feel overwhelming. But the good news is that there are smarter ways to approach your job search today. A LinkedIn job scraper is one of those game-changing web scraping tools that helps you collect all the jobs and all the data you need in minutes. Instead of endlessly scrolling, you can extract data like job titles, job details, company insights, and every job post into one clean Google Sheets file.
In this article, we’ll dive into how LinkedIn scraping works, the legal ways to use it, the best tools available in 2025, a step-by-step guide to get started, and advanced hacks to supercharge your job search.
What is a LinkedIn Job Scraper and How Does It Work?
A LinkedIn job scraper is a tool that automates job hunting by extracting LinkedIn data from any LinkedIn page with vacancies. Instead of manually scrolling, it collects job titles, job details, company names, and job post links, then exports them into Google Sheets or CSV.
The scraping process is simple: search → extract → export → analyze. Unlike manual job search, which is slow and messy, scraping gives you structured job data that reveals patterns and provides valuable insights.
Scrapers generally fall into two categories:
- No-code tools — ready-made apps or cloud platforms that you simply install or access in the browser. They are beginner-friendly and require almost no technical setup.
- Code-based scrapers — executable scripts or open-source projects (often in Python) that you run in your own environment. Some require compiling or manual setup, but they give you much more flexibility and customization.
👉 Both approaches save time, but no-code is easier to start with, while coding tools are better if you need control and scalability.
Is LinkedIn Job Scraping Legal and Safe?
If you scrape LinkedIn job listings, follow LinkedIn’s ToS, local data/privacy laws, and avoid overloading requests to prevent account restrictions.
LinkedIn’s official policy states that automated scraping of LinkedIn profiles or job posts without permission violates their Terms of Service.
The platform uses security measures like rate limiting and blocks to stop bots that scrape data.
That’s why scraping is often a gray area: it depends on what data you collect, how you use it, and where you’re located.
From a legal standpoint, scraping publicly available information (such as company name, job title, or industry) for research is usually safer than collecting personal details.
In many countries, the law focuses on whether you respect user privacy and avoid misusing sensitive data.
To keep your job search or market research safe:
- Use one tool that clearly states it respects user privacy.
- Limit scraping sessions to avoid detection and rate limiting.
- Stick to open job posts and avoid personal profile data.
- Export results into sheets to save time instead of doing time consuming manual copy-paste.
In short, scraping can be safe if done carefully—focusing on public job posts, staying within legal boundaries, and respecting LinkedIn’s rules.
Why People Use LinkedIn Job Scrapers
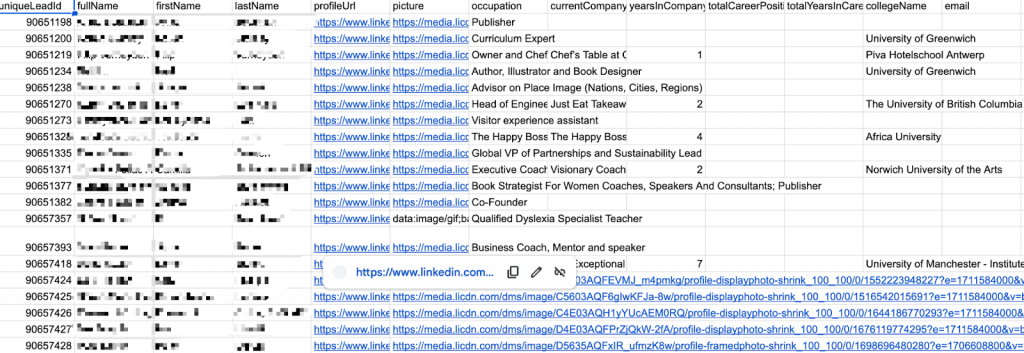
You can scrape LinkedIn job data to pull titles, companies, locations, and links into a clean CSV/Google Sheets, speeding up your search. You can scrape LinkedIn job posts when analyzing career trends.
Why is this relevant in 2025? Because recruiters post thousands of opportunities daily, and the best ones disappear fast. Having structured job data gives job seekers a big advantage: you can compare roles, track your career progression, and spot patterns in job titles and industries that match your skills.
You can scrape LinkedIn jobs data to quickly gather large sets of openings, helping track hiring trends, talent demand, and competitor activity.
This approach isn’t only for job seekers—it’s equally useful for HR professionals, career coaches, and freelancers who want to analyze markets, discover opportunities, or tailor applications with precision. With the right web scraping tools, you can turn scattered posts into an actionable strategy.
Faster job search & data collection
A LinkedIn job scraper helps job seekers move beyond manual scrolling. Instead of clicking “next page” endlessly, you can scrape data from multiple LinkedIn profiles and job posts at once.
With an intuitive interface or a user-friendly interface, it’s easier to spot patterns across roles and companies, so you only focus on the opportunities that matter. Scrolling LinkedIn manually means wasting hours on jobs that look relevant at first glance but turn out to be outdated, duplicated, or simply clickbait listings from agencies.
Competitive intelligence (monitoring competitors & recruiters)
Companies and professionals use scraping for monitoring. For example, recruiters track which competitors are hiring, which job titles are trending, and how often roles appear. This provides valuable insights into hiring activity and makes it easier to prepare a smarter strategy.
Lead generation for recruiters
For HR teams, scraping is not just about jobs—it’s about people. By targeting a URL with LinkedIn profiles, one tool can collect candidate details to build lead lists faster.
Independent recruiters often start by scraping job posts to filter out irrelevant or low-quality listings (“junk” roles) and identify what an “ideal candidate” for a given role looks like.
Once they have a clear benchmark, the next step is scraping LinkedIn profiles to build candidate lists and match people with those roles.
With legal considerations in mind and tools that respect user privacy, recruiters can scale outreach while staying compliant.
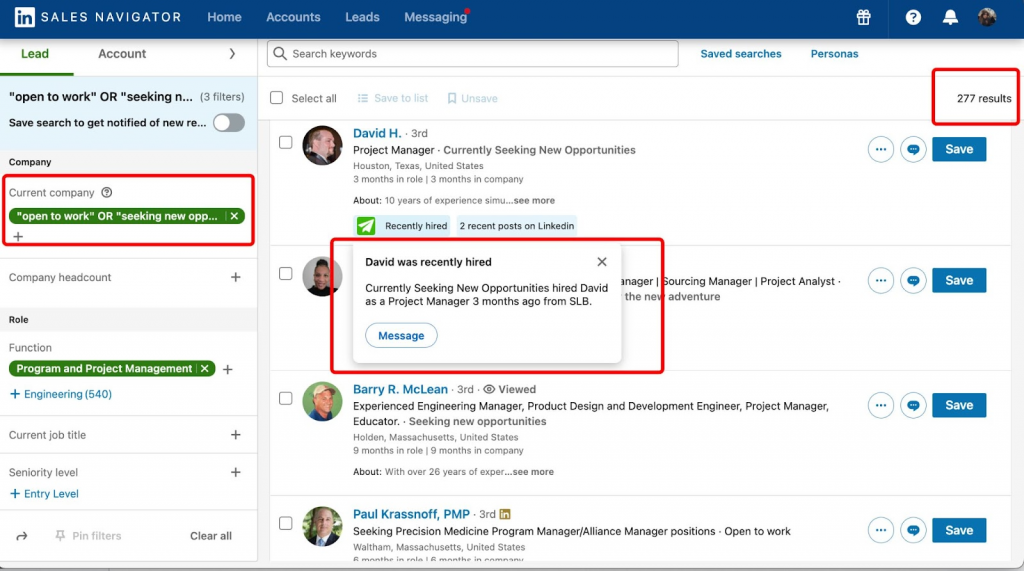
Pair a linkedin jobs scraper with Sales Navigator filters for cleaner, more targeted leads.
Market research
Beyond job hunting, scraping is useful for market research. Analysts can track hiring demand, industry shifts, and location trends. One such tool even allows exporting data into dashboards, helping companies plan expansion, benchmark salaries, and understand workforce needs.
3 Approaches to Scraping LinkedIn Jobs
To scrape LinkedIn job posts, use special tools for descriptions, then rely on Linked Helper for outreach automation.
Two Scraping Modes
- Using your account: Any tool (automation, extension, or script) logs in as you and scrapes jobs tied to your LinkedIn session. Downside: can hit action limits, account risk if overused.
- Without login: Some scrapers pull public job listings visible even when not logged in (see screenshot 1). Safer for your account, but usually less detailed.
Using automation tools (easiest)
Dedicated software and SaaS scrapers let you collect job data—like job title, location, industry, salaries, and description—without coding. They usually create structured exports (CSV, Google Sheets) and come with dashboards to analyze results. The main advantage is speed and ease of access, but many are paid and limited for public use only.
Examples:
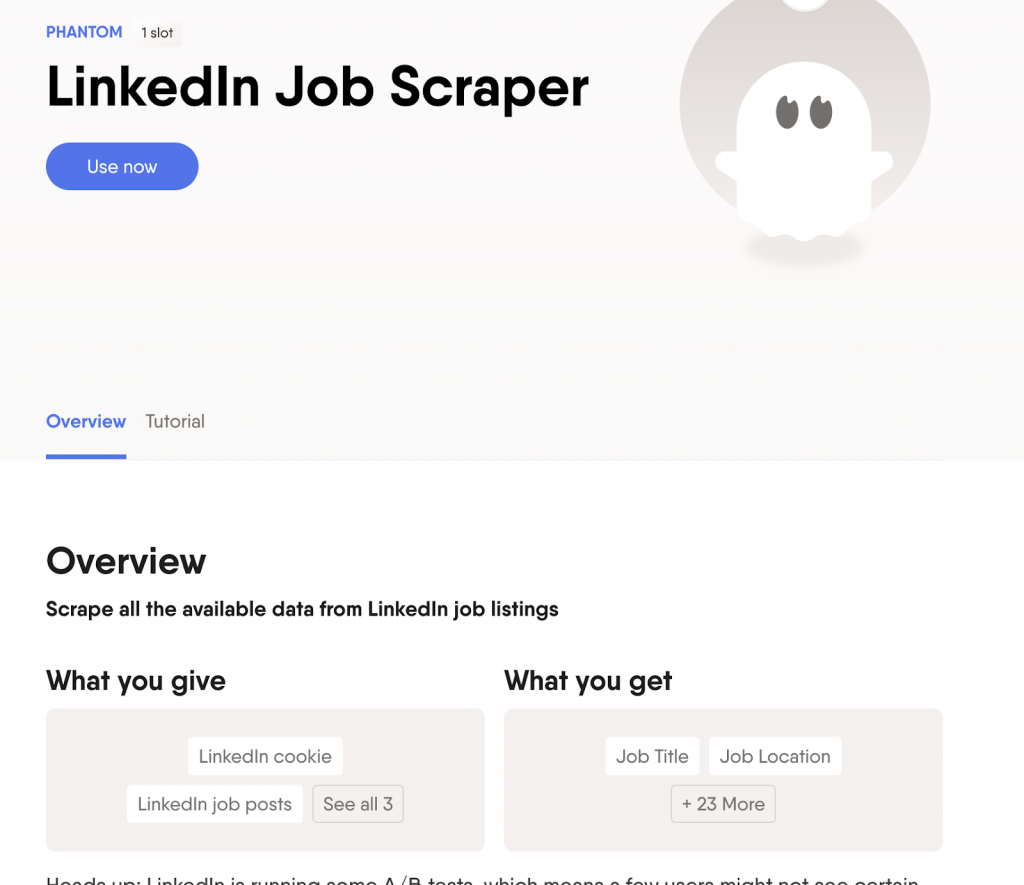
- PhantomBuster – cloud scraper with LinkedIn job templates.
- TexAu – SaaS platform for jobs + candidate scraping.
- Octoparse – no-code desktop scraper with visual workflow builder.
✅ Pros: no coding, scalable, beginner-friendly.
❌ Cons: usually paid, limited mostly to public data.
Using browser extensions
A lighter option is installing a scraper extension on your browser. These tools work directly on the website and allow you to extract jobs across multiple pages with just a few clicks.
Cons: they often break when LinkedIn changes its layout and
✅ Pros:
- Easy to install and start using
- Affordable (many have free plans)
- Works well for small datasets
❌ Cons:
- Can break when LinkedIn changes its layout
- May struggle with larger datasets or next page navigation.
- Limited export capacity compared to SaaS
Examples:
- DataMiner – scrape job listings from search results.
- Instant Data Scraper – free Chrome extension for quick tables.
- Web Scraper.io – browser-based visual scraper.
Writing Python scripts (for developers)
Tech-savvy users can create their own scrapers with Python libraries like BeautifulSoup or Selenium. This gives full control—custom fields, targeted URLs, even filtering by location, industry, or job description. The downside: it’s time-consuming, requires coding skills, and may run into blocking rules.
Examples:
- Selenium + BeautifulSoup – automate page navigation and parsing.
- PyLinkedinScraper (open source).
- Bright Data DIY scripts (cloud proxies + Python).
✅ Pros: full flexibility, free/open source options, no SaaS limits.
❌ Cons: steep learning curve, time-consuming, risk of LinkedIn blocking if not careful.
How to Combine Linked Helper with Job Scraping Tools
Linked Helper 2 doesn’t scrape job posts directly, but it becomes powerful when paired with job scraping tools like PhantomBuster, TexAu, or Octoparse. The idea: one tool collects vacancy data, the other helps you find and reach the people behind those jobs.
Example 1: Independent Recruiter Workflow
- Scrape vacancies with PhantomBuster (e.g., “Senior React Developer in Berlin”) → extract role requirements.
- Use Linked Helper to search for matching candidate profiles and scrape their details.
- Cross-analyze job descriptions and candidate data to spot top talent.
- Match candidates with companies posting those jobs and pitch your services.
Example 2: Candidate or Recruiter Outreach
- Job seeker scrapes job listings (title, company, posting link) with TexAu or Octoparse.
- They upload the list of companies into Linked Helper’s Employees Extractor → collect recruiters or hiring managers.
- Outreach: instead of just clicking “Easy Apply,” they connect and message recruiters directly, standing out among other applicants.
💡 Variant for independent recruiters: scrape jobs from smaller companies, then use Linked Helper to extract CEOs or HR contacts and pitch them both your ideal candidate and your recruiting services.
Why This Combo Works
- Scrapers = structured job data at scale (vacancies, requirements, companies).
- Linked Helper = structured people data + automated outreach (recruiters, employees, candidates).
- Together, they turn unstructured job boards into a full lead pipeline: from vacancy → to candidate → to conversation.
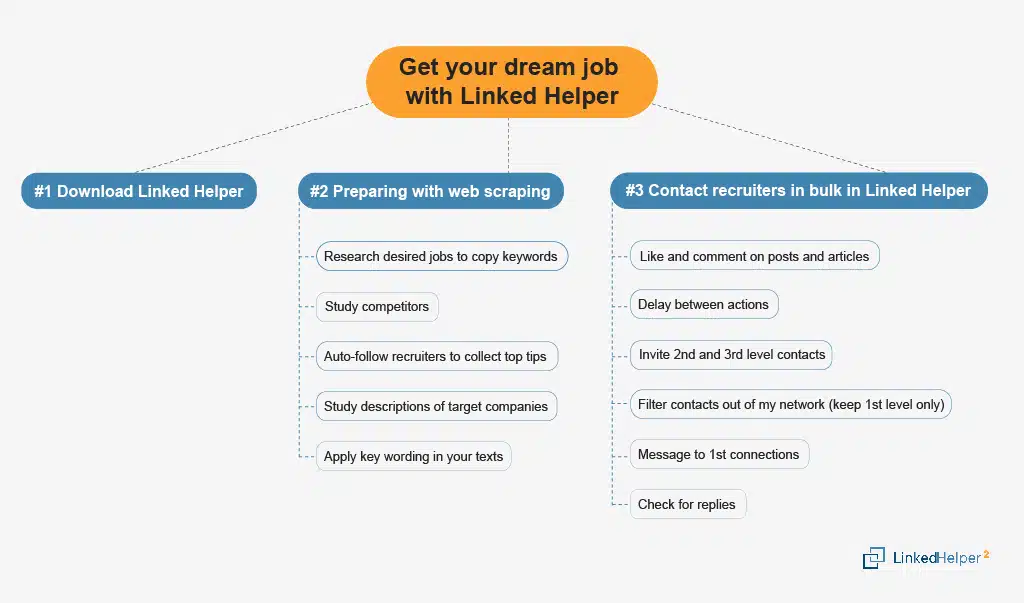
Step 1 – Install Linked Helper (free trial available)
Download Linked Helper, a proven automation software for LinkedIn. It can help you find leads, promote your profile, and automate job search tasks.
💡 Tip: Use the 14-day free trial of Linked Helper along with the 30-day Sales Navigator trial. This combo lets you filter recruiters who posted in the last 30–90 days and discover more active opportunities.
Step 2 – Set your job search criteria
Before scraping, research your target job descriptions:
- Collect keywords from at least 6–8 job posts.
- Update your LinkedIn profile, Skills, and CV with these phrases.
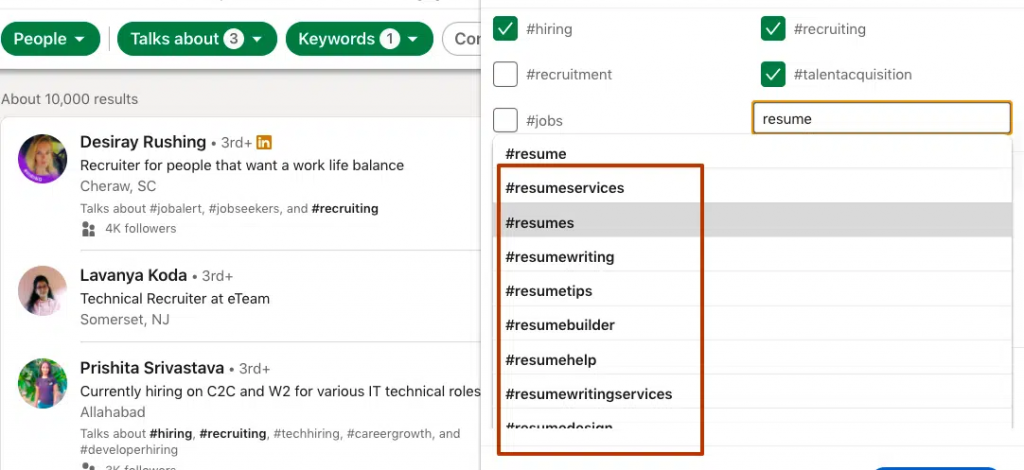
- Use Boolean search (e.g., “Job alert AND Marketing”) to uncover more job posts.
You can also analyze competitors with the “Visit & Extract” action to receive a CSV file of their LinkedIn profiles, descriptions, and skills.

This helps position your CV and highlight your unique strengths.
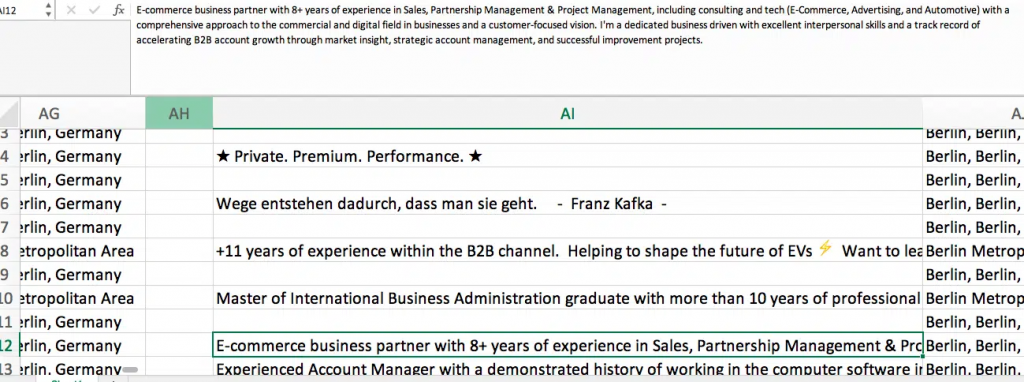
Step 3 – Extract recruiter info
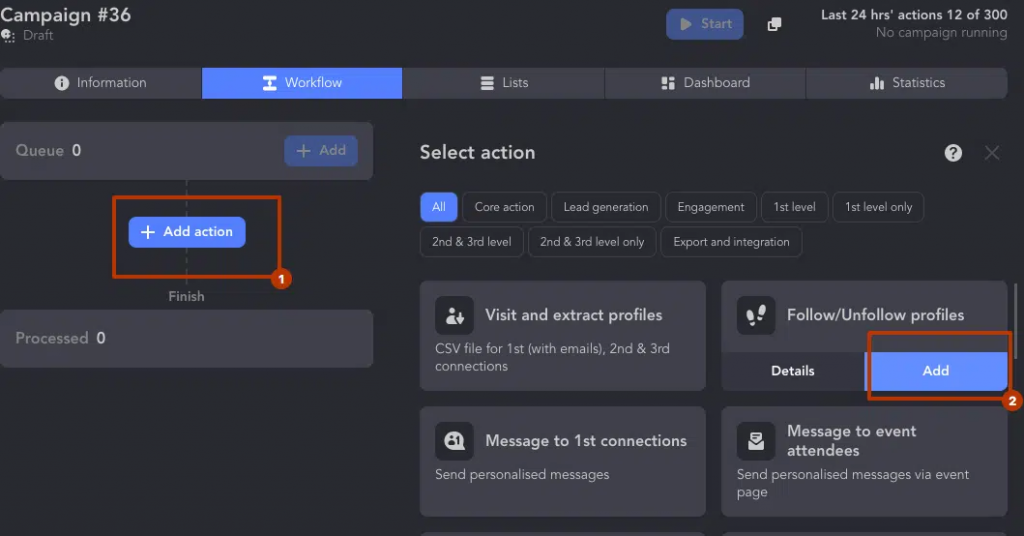
With Linked Helper, you can:
- Auto-follow recruiters to get fresh job tips in your feed.
- Collect data on recruiters and companies (name, industry, location, job requirements).
- Save insights into CSV or Excel for structured analysis.
This saves you from the time consuming manual process and gives a clear overview of trends in your target market.
Step 4 – Save to CSV or Excel for analysis
Once you’ve scraped recruiter and company data, export everything into CSV or Excel. This gives you structured information—company name, industry, location, job description—that you can easily filter and analyze. Instead of messy copy-paste, you’ll have clean datasets ready to compare and apply in your job search.
Step 5 – Automate recruiter outreach
After analysis, it’s time to act. With Linked Helper, you can automate the entire outreach process:
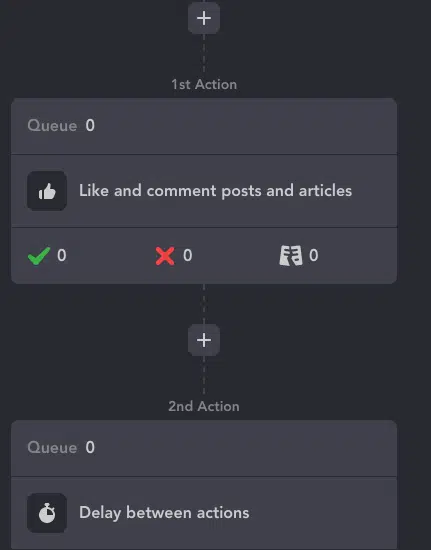
- Like & comment on recruiter posts to get noticed.
- Pause to give them time to see your profile.
- Send invites with a short, polite intro message.
- Follow up with 1st-degree connections who accept.
- Use free InMails to reach “Open” profiles outside your network.
This flow makes your approach natural while saving hours of manual effort.
Pro Step – Linked Helper campaign example for bulk recruiter outreach
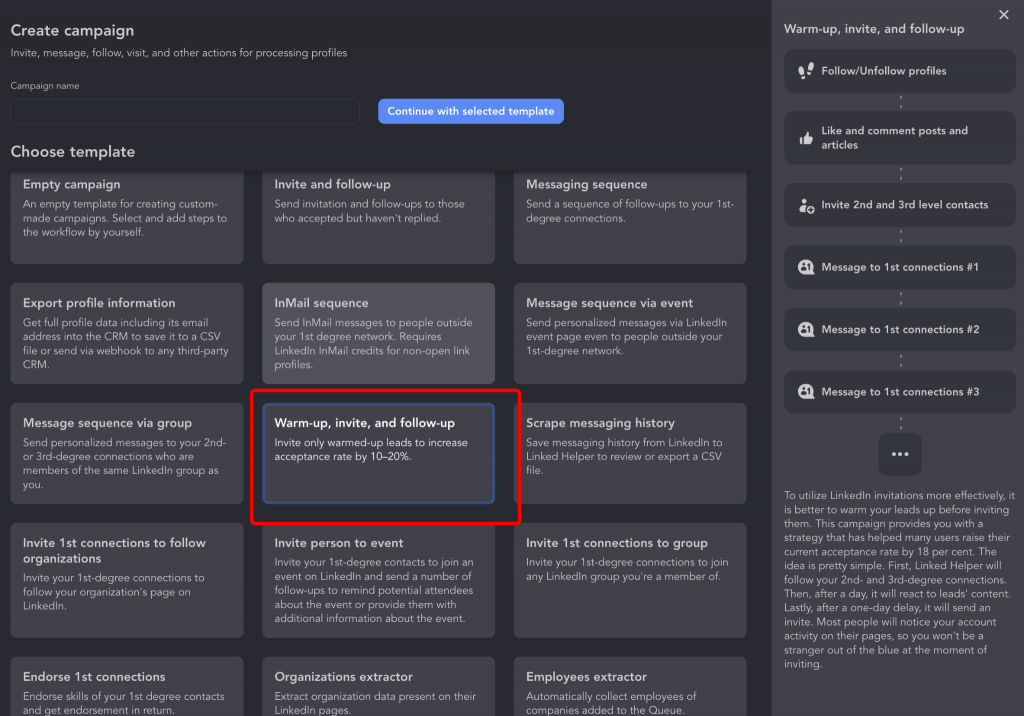
For a more advanced setup, create a smart campaign such as “Invite & Follow-Up.” This allows you to connect with target recruiters and automatically send a short welcome message.
How to structure your campaign:
- Like and comment on posts from recruiters.
- Add delays between actions to avoid spam detection.
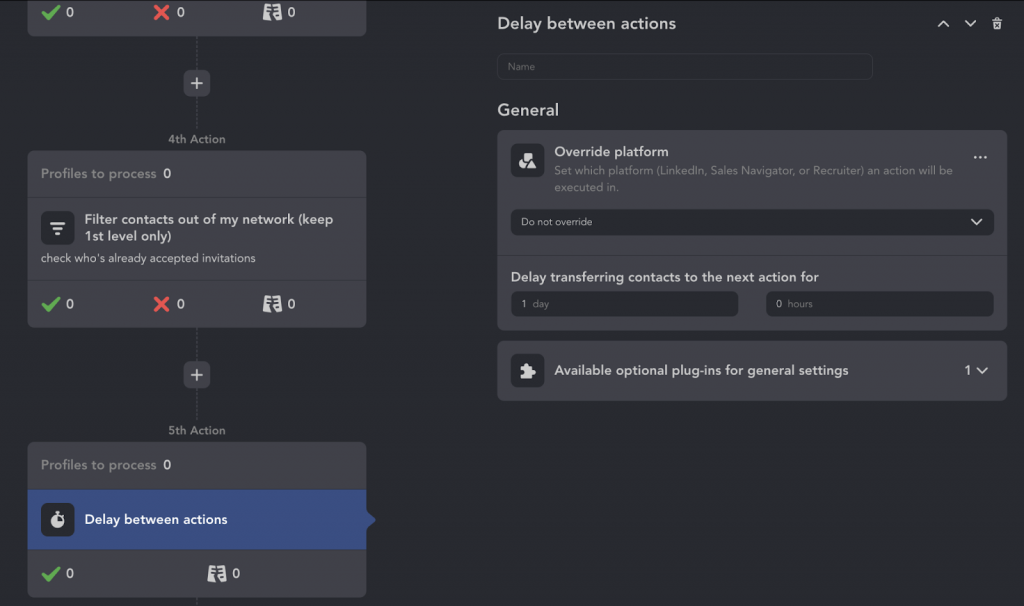
- Invite 2nd- and 3rd-level recruiters (filter out 1st-degree).
- Send tailored follow-ups only after a connection request is accepted.
- Check replies and continue conversations naturally.
💡 Use keywords like “Recruiter” or “Talent Acquisition Manager” in your LinkedIn search. Avoid “Hiring Manager”—they usually pass tasks to recruiters and are less responsive.
👉 Remember: don’t overload your first message with a full CV. Keep it short, show interest, and only share more details once the recruiter replies. This is the key to building trust and getting real results.
Tips to Maximize Success with LinkedIn Job Scraping
Optimize your LinkedIn profile before outreach
Before you start scraping and applying, make sure your profile picture, current job title, and headline look professional. A polished profile page builds trust and increases your chances of getting responses.
Use keyword-rich titles and descriptions in your resume
Recruiters search by job role, skills, and company name. Add a promotion, highlight career progression, and list key achievements with relevant keywords to appear in more searches.
Track applications and responses
Keep a simple tracker for applications, employment type, and networking opportunities. This helps you measure what works, follow up on promising leads, and refine your approach.
Avoid spammy behavior to prevent restrictions
LinkedIn can restrict accounts that overuse scraping or automation. Stay under safe limits, mix manual activity with automation, and focus on personal brand building instead of bulk outreach.
Tips for Recruiters
If you’re a recruiter, here are a few practical ways to speed up sourcing with scraping tools:
- Use multiple scrapers at once – Running two or three job scraping tools in parallel helps you cross-check vacancies, filter out low-quality ones, and build a cleaner dataset.
- Accelerate candidate scraping with multi-account setups – In tools like Linked Helper 2, you can add several LinkedIn accounts to scrape candidate profiles faster.
- Leverage paid + free LinkedIn accounts together – If you have a premium LinkedIn account, you can scrape leads there, export them via CSV, and then continue processing or messaging them from a free LinkedIn account. This way you maximize reach without hitting limits too quickly.
- Switch platforms strategically – Sometimes moving scraped leads between platforms (e.g., LinkedIn → CRM → outreach tool) gives more flexibility and helps you avoid being flagged.
- Personalize your outreach – When you contact scraped leads, personalization in your first message can significantly increase reply rates compared to generic templates.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Scraping LinkedIn Jobs
Overloading requests (risk of block)
Sending too many scraping requests in a short time can trigger LinkedIn’s anti-bot systems, leading to account restrictions.
How to avoid: Use throttling, rotate IPs, and keep request frequency natural.
Ignoring personalization in outreach
Using scraped job data for generic mass messages reduces response rates and harms your credibility.
How to avoid: Customize each message with the company name, job title, or mutual connections.
Using your personal LinkedIn account with unsafe tools
Relying on Chrome extensions or shady scraping tools that directly connect to your personal account is risky. Many of them store your credentials and can compromise your account security.
How to avoid: Use only trusted, professional-grade tools. Keep your main account safe and consider using a dedicated account for automation.
Overusing your account (too many requests)
Sending hundreds of scraping requests in a short time can trigger LinkedIn’s anti-bot detection, leading to restrictions or bans.
How to avoid: Throttle your requests, rotate IPs, and mimic human browsing behavior.
Scraping from your own IP
Running heavy scraping from your home or office IP makes it easy for LinkedIn to detect and block you.
How to avoid: Use quality proxies or cloud-based scraping tools that handle IP rotation.
Blind trust in free tools
Many “free” tools exploit your account, steal login data, or operate in ways that put your account at risk.
How to avoid: Always research tools before use. Avoid extensions or services that require direct LinkedIn login without transparency.
Not cleaning your scraped data
Raw scraped data often contains duplicates, incomplete fields, or outdated postings.
How to avoid: Regularly clean and validate your data before using it for outreach or analysis.
Conclusion: Choose the Right LinkedIn Job Scraper for Your Needs
Scraping LinkedIn jobs lets you capture job title, company, location, salary, description, posting date, and job URL at scale and export to CSV/Google Sheets for analysis.
Linked Helper is a solid choice if your main goal is to collect structured data such as profiles, companies, and leads for outreach. It works well for sales teams, recruiters, and marketers who need scalable automation and easy integration with LinkedIn. However, it’s important to note that Linked Helper does not scrape post content or job descriptions.
If your priority is analyzing LinkedIn job postings or extracting text from posts for content insights, sentiment analysis, or market research, you may want to consider other tools like PhantomBuster, Scraping Dog. These platforms are better suited for scraping textual content and specific job listings.
In short:
- Use Linked Helper for outreach, lead collection, and campaign automation.
- Use PhantomBuster, Octoparse for scraping job descriptions and post texts.

👉 Ready to streamline your LinkedIn outreach? Try Linked Helper for free today and see how it can boost your productivity.
FAQ About LinkedIn Job Scrapers
Is LinkedIn scraping illegal?
Scraping LinkedIn data without permission violates its Terms of Service, but whether it’s illegal depends on the laws in your country.
Will LinkedIn ban you for scraping?
No. But LinkedIn actively detects and restricts accounts that use unauthorized scrapers.
Can ChatGPT scrape LinkedIn?
No. ChatGPT cannot scrape LinkedIn. It can only explain how tools work and provide guidance.
Is there a LinkedIn scraper?
Yes. Tools like Linked Helper, Phantombuster, and Octoparse offer scraping features.